The challenge is open. Time left: almost 2 years (31 Dec 00:00)
Meetween
Unlock the Future of Speech Technology
Explore our innovative AI solutions that empower seamless communication and drive progress in the field of speech technology.
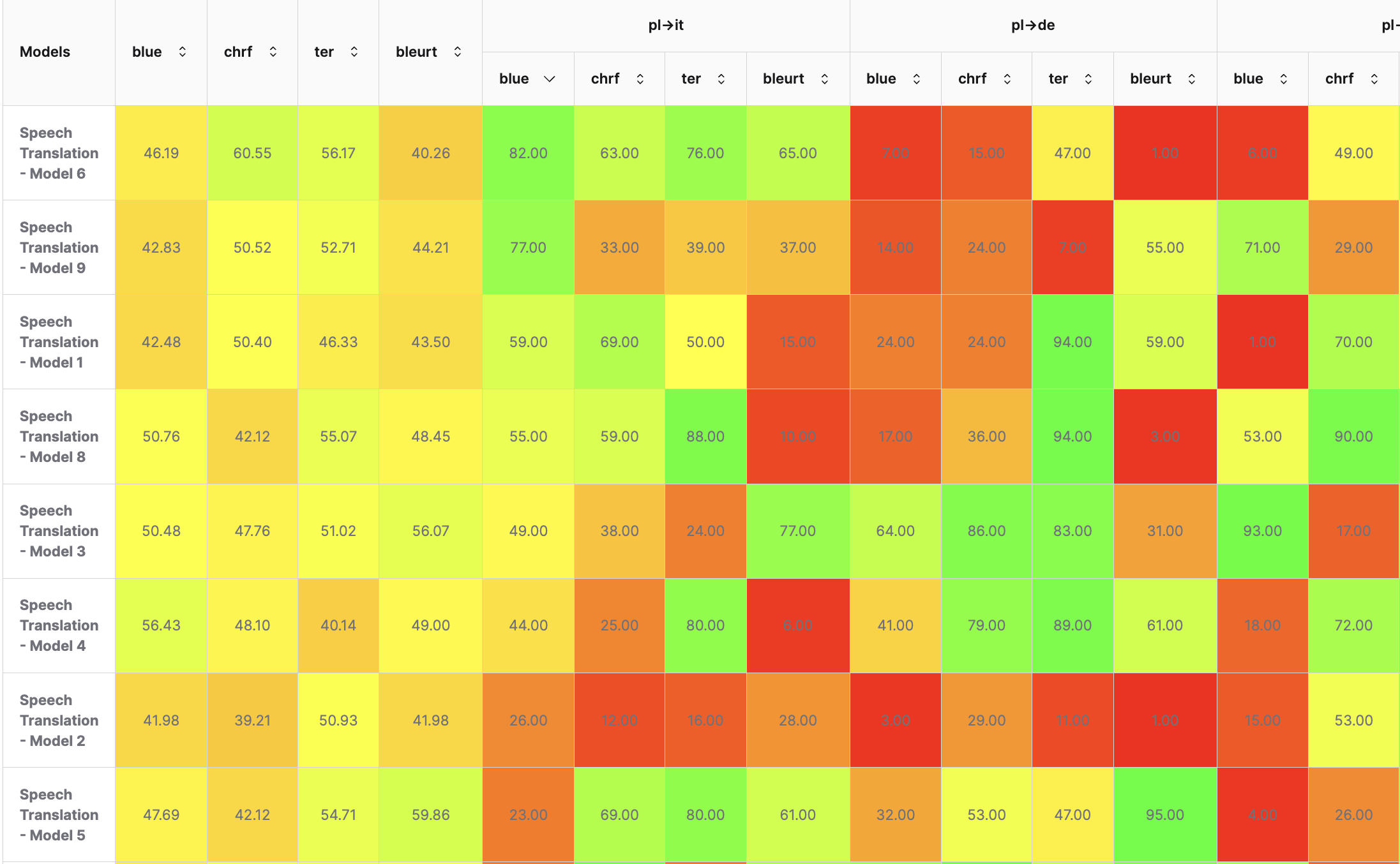
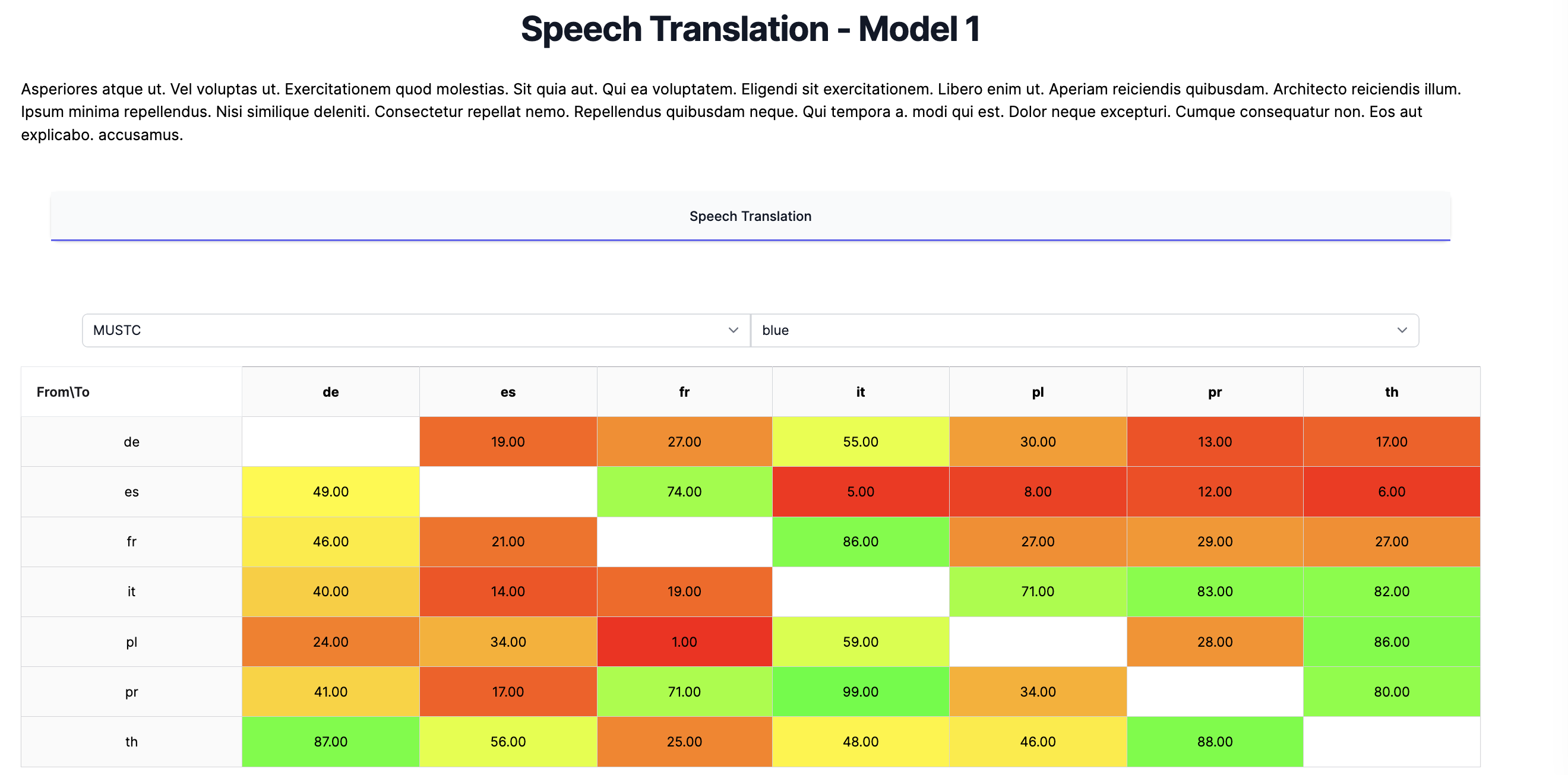
73
models
14
test sets
70
metrics
Key Tasks in NLP and Speech Technology
Explore the core functions that enhance communication through language understanding, translation, and speech recognition.
-
Machine translation (MT)
Converts text from one language to another, maintaining the meaning and context of the original message. This task involves translating between languages like English to French or Polish to Spanish and aims to ensure both grammatical and semantic accuracy.
-
Summarization (SUM)
Summarization is the task of generating concise versions of longer texts while preserving the most important information and main ideas. It can be either extractive (selecting key sentences) or abstractive (creating new sentences).
-
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
Converts spoken language into written text by processing audio inputs. ASR systems are widely used in applications like transcription, virtual assistants, and speech-to-text services. interaction.
-
Speech Translation (ST)
Converts spoken language from one language into spoken or written output in another language in real time or offline. This task combines ASR, machine translation, and TTS to facilitate seamless communication across language barriers, often used in live conversations, broadcasts, or conferences.
-
Speech Sumarization (SSUM)
Produces summaries directly from spoken content, such as meetings or lectures, eliminating the need for full transcription and helping users quickly grasp key points from audio sources.
-
Speech Question-Anwering (SQA)
Enables interactive systems to answer questions based on spoken inputs or audio sources, combining ASR with natural language understanding to deliver accurate, real-time responses.
-
Spoken Language Understanding (SLU)
Analyzes spoken language to extract meaning, intents, or commands. SLU powers voice assistants and dialogue systems by interpreting user speech for appropriate action or resdalej nie powiedziałeś w którym ponse.
-
Lip Reading (LIPREAD)
Recognizes spoken words by analyzing lip movements in video inputs, useful in noisy environments or for accessibility purposes, such as assisting hearing-impaired individuals.
-
Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Converts written text into natural-sounding speech, facilitating applications like audiobooks, virtual assistants, and accessibility tools for visually impaired users.